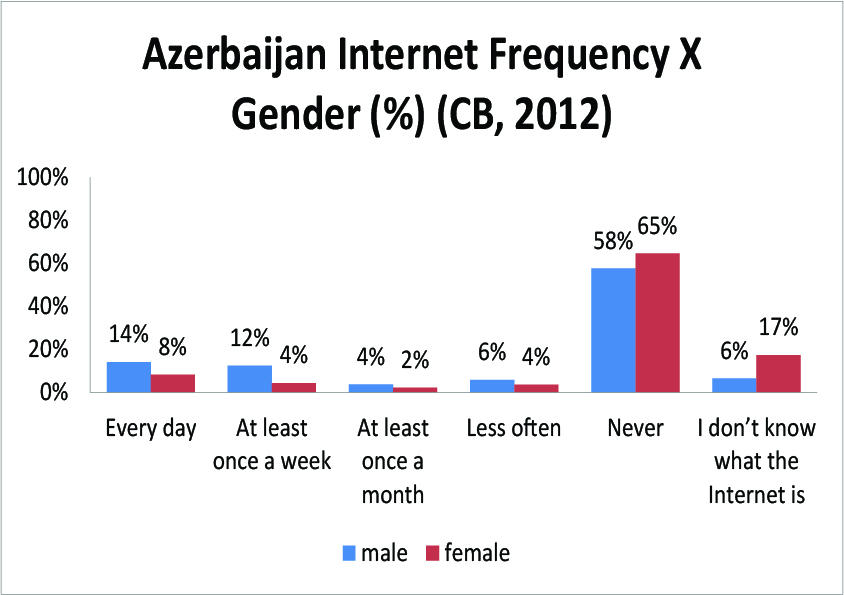
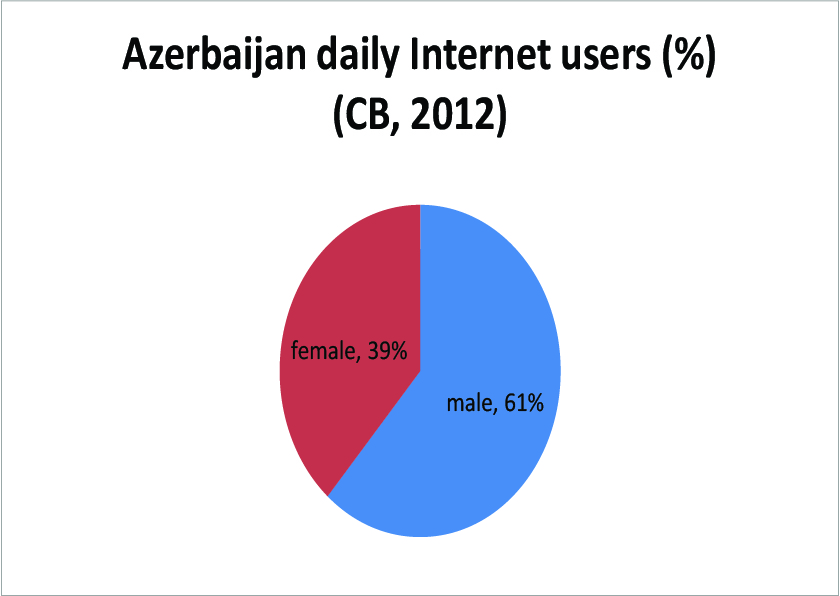
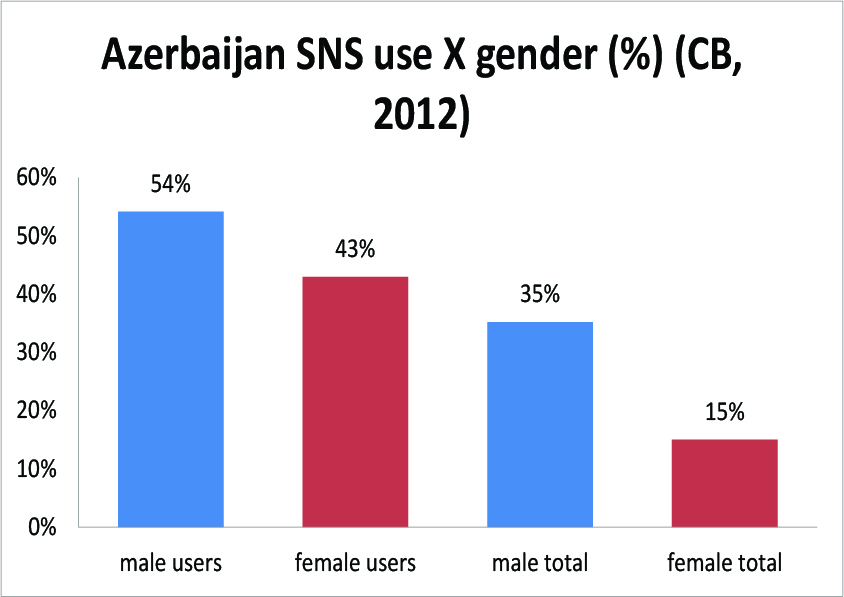
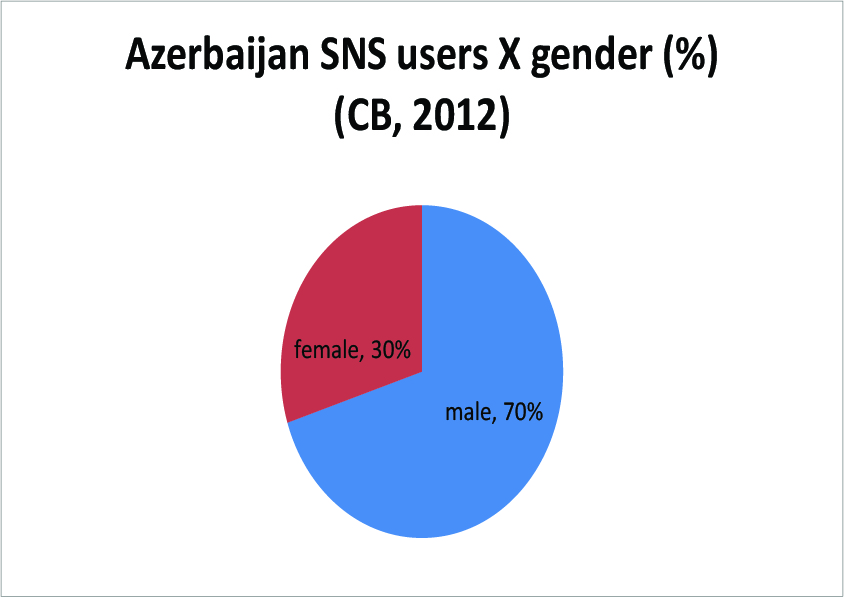
This is an update to this post about 2011. 2012 overall Internet use here.
All data is from the Caucasus Barometer.
We know that a larger percentage of Armenians (52%) and Georgians (43%) are online than Azerbaijanis (27%) and weekly or more often adult Internet users are 43% of Armenians, 33% of Georgians, and 19% of Azerbaijanis.
Armenia has 3,100,236 people, Azerbaijan 9,168,000 people, and Georgia 4,486,000 people – but that’s total population, we need to look at just adults (since that’s the data we have about Internet use – I fully acknowledge that teenagers are online and may be using social media). According to the World Bank, 20% of Armenians, 21% of Azerbaijanis, and 17% of Georgians are ages 0-14.
So, let’s take them out of the equation – (that’s 620,047 Armenians, 1,925,280 Azerbaijanis, and 762,620 Georgians) – and you have “adult” populations of 2,480,189 AM, 7,242,720 AZ, and 3,723,380 GE. So raw weekly or daily Internet users would be:
744,057 in 2011 and 1,289,698 in 2012 Armenia
941,554 in 2011 and 1,376,117 in 2012 Azerbaijan
1,042,546 in 2011 and 1,228,715 in 2012 Georgia
Thus in 2012, there are about 1.2-1.4 million weekly or daily Internet users in each country, with Azerbaijan having the most in raw numbers, despite the lowest percentage.

In 2011, 6% of Armenians, 7% of Azerbaijanis, and 9% of Georgians (ADULTS) were on Facebook (let’s leave Odnoklassniki out of this for now). In 2012, 27% of Armenians, 13% of Azerbaijanis, and 30% of Georgians were on a social networking site.
Raw numbers then would be:
148,811 in 2011 and 669,651 in 2012 in Armenia
506,990 in 2011 and 941,554 in 2012 in Azerbaijan
335,104 in 2011 and 1,117,014 in 2012 in Georgia

—
Socialbakers.com is a website that gives Facebook statistics. I’m not very comfortable using it because of its lack of transparency and because we don’t know where they get any of their data, but let’s see what they say.
ARMENIA
Total Facebook Users 395340 — I have 669,651 adults, so this seems off (although Odnoklassniki could be a factor)
Position in the list 112
Penetration of population 13.32% — I have 27% of adults
Penetration of online population 29.06% — I have 53% of adults
AZERBAIJAN
Total Facebook Users 1013080 — I have 941,554 adults, so this seems reasonable
Position in the list 82
Penetration of population 12.20% — I have 13% of adults, so this seems a little low for total population
Penetration of online population 23.97% — I have 50% of adults, so this seems really off
GEORGIA
Total Facebook Users 969840 — 1,117,014 adults, so this seems fairly close
Position in the list 85
Penetration of population 20.95% — I have 30% of adults, so this is off
Penetration of online population 82.84% — I have 70% of adults, so this seems okay
In the future I’ll look at socialbaker’s gender and age breakdown and see if it matches with what comes from the Caucasus Barometer.
—
(This is a copy and paste from what I wrote about 2011, but I wrote it in winter 2012.)
Okay, so back to my original point — I’ve noticed that the Azerbaijani Facebook and Twitter worlds is substantially more active than the Armenian one. (I acknowledge that I’m not up on what is going on in Georgia, but for reasons explained below, you’ll see that it is probably similar to Armenia). Why is this?
1. The raw numbers noted above — a lot more Azerbaijanis are on Facebook than Armenians. (I’m going to leave these countries’ diasporas out of this, but for what it’s worth, I feel like the Azerbaijani diaspora engages with Republic of Azerbaijan citizens more than Armenian diaspora do with Republic of Armenia citizens).
2. Because of the lack of free expression and assembly in Azerbaijan, most political discussion takes place on Facebook. Armenians can do this fairly freely in cafes or homes. Similarly, Armenians can organize and be political active in ways that Azerbaijanis cannot.
3. Language is a big part of this. As I wrote before, users of the Azerbaijani language are at a serious advantage over users of Armenian or Georgian because Azerbaijani uses the Latin script. This is also a special concern when it comes to Twitter and even more so when it comes to mobile phones (only the most recent Android OS has Armenian and Georgian, iPhone has it, but the others? No way). But my overall point is that there are barriers to Armenians and Georgians using these sites.
4. This is entirely speculative, but I get the sense that Bakuvians are just way more wired than Yerevantsis are. The Baku social media scene, beyond politics, is always jumpin’! There are a ton of Azerbaijani Instagrammers, Pinteresters, and other social media platform users. I just don’t see that same sort of scene in Yerevan. Yes, there is a bit of a FourSquare scene and of course people use these social media sites, but not to the extent that I see in Azerbaijan. (Although this may be a result of the sheer numbers!!)
I’m sure there are other reasons, and I’d love to hear comments…